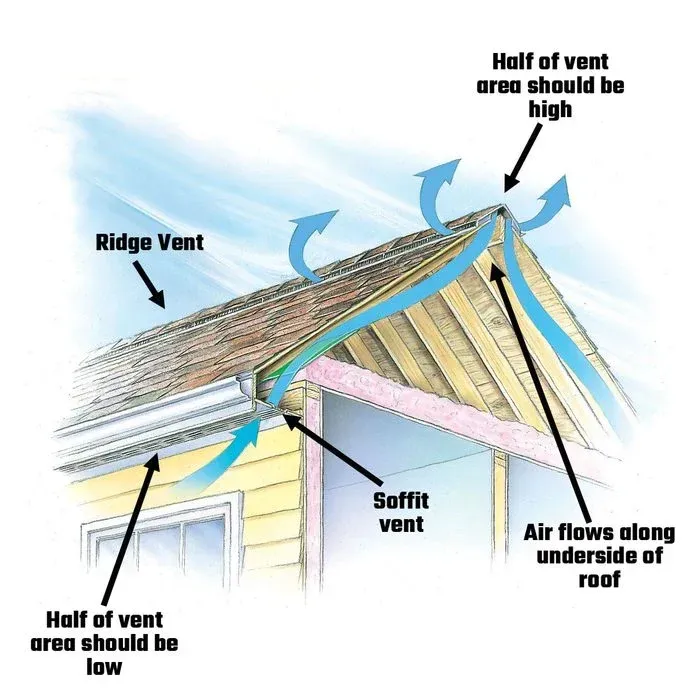
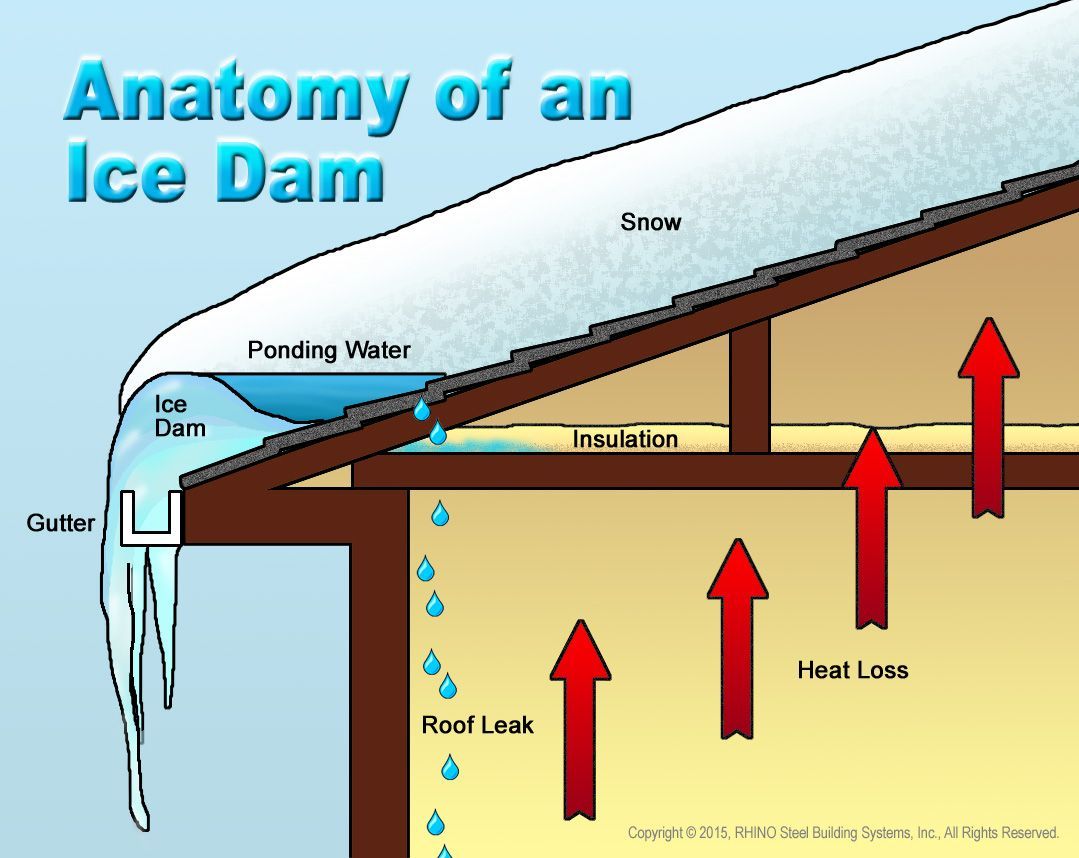
Get in touch
30-614-9525
Service@HofRoofingOhio.com
GET A FREE QUOTE TODAY - Cleveland (440) 409-4689 | Akron/Canton (330) 614-9525
Styles of roofs
What style is your home?

Styles of Roofs: A Comprehensive Overview
Roofs, the crowning glory of any structure, serve both functional and aesthetic purposes. They protect buildings from the elements, provide insulation, and contribute significantly to the overall architectural style. This essay will delve into the various styles of roofs, exploring their unique characteristics, historical origins, and modern applications.
Flat Roofs
Flat roofs, as the name suggests, have a minimal slope or are completely horizontal. They are commonly found in regions with mild climates, as they offer a larger surface area for solar panels and rooftop gardens. Historically, flat roofs were prevalent in ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Mesopotamians, who used them to create terraces for social gatherings and astronomical observations.
In modern construction, flat roofs are often used in commercial buildings, such as warehouses and office complexes. They are typically constructed using a combination of concrete slabs, insulation, and waterproofing membranes. While flat roofs are known for their simplicity, they require regular maintenance to prevent water leaks and ensure structural integrity.
Gabled Roofs
Gabled roofs, characterized by two sloping sides that meet at a ridge, are one of the most common roof styles worldwide. The triangular shape formed by the sloping sides allows for efficient rainwater runoff and provides additional headroom within the attic space. Gabled roofs have been used for centuries, and their versatility has made them popular in various architectural styles, from traditional cottages to contemporary homes.
Gabled roofs can be further classified based on the angle of the slopes. Steeply sloped gabled roofs are often found in regions with heavy snowfall, as the steep pitch helps to shed snow more effectively. Shallowly sloped gabled roofs, on the other hand, are more common in regions with milder climates and are often used to create a more contemporary aesthetic.
Hip Roofs
Hip roofs feature sloping sides on all four sides, creating a pyramid-like shape. They are known for their strength and stability, making them a popular choice for regions prone to severe weather conditions. Hip roofs also offer a larger attic space compared to gabled roofs, providing additional storage or living area.
Hip roofs can be further customized with dormers, which are projections from the roofline that provide additional natural light and ventilation. Dormer windows can be designed in various shapes, including gable, hip, and flat.
Gambrel Roofs
Gambrel roofs, also known as barn roofs, are characterized by two pairs of sloping sides, with the lower slopes being steeper than the upper slopes. This design creates a unique and distinctive appearance, often associated with rural architecture. Gambrel roofs are commonly found in barns, stables, and other agricultural buildings.
The steeper lower slopes of a gambrel roof provide additional headroom within the attic space, making it ideal for storing hay, equipment, or even converting into living quarters. The shallower upper slopes help to shed snow and rainwater more efficiently.
Mansard Roofs
Mansard roofs, also known as curb roofs, are similar to gambrel roofs but have a more pronounced curve at the bottom of the upper slopes. This creates a distinctive silhouette and provides additional attic space. Mansard roofs are often found in historic buildings and are popular in regions with cold winters, as the curved shape helps to shed snow and ice.
Mansard roofs can be further customized with dormers and other architectural elements to create a unique and visually appealing design.
Conclusion
The choice of roof style is a crucial decision in the design and construction of any building. The style not only affects the appearance of the structure but also influences its functionality, energy efficiency, and overall durability. By understanding the various roof styles and their unique characteristics, architects, builders, and homeowners can make informed decisions to create beautiful and functional structures that withstand the test of time.